Discover the secrets of the past like never before, with the help of cutting-edge technology. LiDAR in archaeology is revolutionizing the way we uncover ancient civilizations and hidden treasures. By utilizing advanced drone scanning, researchers can now map the earth’s surface with unprecedented detail, shedding light on the mysteries that have eluded us for centuries. In this article, we’ll explore how LiDAR drone scanning is changing archaeology and bringing the past to life.
Key Takeaways
- LiDAR Drone Scanning in Archaeology: Revolutionizing archaeological discovery and research.
- Non-Invasive Exploration: Enables detailed mapping without disturbing sites.
- Discovering Hidden Structures: Unveils structures obscured by vegetation or terrain.
- Enhancing Archaeological Research: Provides precise 3D models for in-depth analysis.
- Efficiency: Covers large areas quickly, enhancing project timelines.
- Conservation Efforts: Supports preservation by identifying vulnerable sites.
What is LiDAR in Archaeology?
LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing technology that uses laser pulses to measure the distance between a sensor and the Earth’s surface. In the field of archaeology, LiDAR is employed to create detailed, high-resolution maps of archaeological sites and their surrounding landscapes. By integrating LiDAR technology with drones, researchers can obtain aerial data of large areas in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods.
Brief Explanation of LiDAR Technology
The core of LiDAR technology lies in its ability to emit thousands of laser pulses per second. These pulses travel to the Earth’s surface and bounce back to the sensor, which then calculates the distance based on the time it took for the pulse to return. By collecting millions of these distance measurements, or “points,” a precise and accurate 3D model of the terrain is generated. This 3D model, known as a point cloud, can be processed further to remove vegetation and other surface features, revealing the underlying landscape and potential archaeological structures.
The Role of Drones in LiDAR Data Collection
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), have become an essential tool for collecting LiDAR data in archaeology. Equipped with LiDAR sensors, drones can fly over vast archaeological sites, capturing high-resolution data with unparalleled precision. This aerial perspective enables researchers to identify and map previously undiscovered features, such as hidden structures, ancient road networks, and agricultural systems, providing valuable insights into the lives of past civilizations.
How Does LiDAR Work in Archaeology?
Airborne LiDAR and Archaeology
Airborne LiDAR involves mounting a LiDAR sensor on an aircraft or drone to capture data from above. This approach allows archaeologists to cover large areas quickly and efficiently, making it ideal for surveying remote or inaccessible sites. As the drone flies over the terrain, it collects a dense array of elevation data points, which can be processed into a digital elevation model (DEM). This DEM can then be analyzed to identify archaeological features, such as building foundations, walls, and other structures that may be obscured by vegetation or soil.
Ground-Based LiDAR for 3D Reconstructions
Ground-based LiDAR, also known as terrestrial laser scanning (TLS), is a method used to capture detailed 3D data of archaeological sites at ground level. By placing the LiDAR sensor on a tripod, researchers can scan individual structures, artifacts, or excavation areas with incredible precision. The resulting point cloud data can then be used to create accurate 3D reconstructions of the site, aiding in the documentation and analysis of archaeological findings.
LiDAR Mapping of Ancient Structures
LiDAR mapping involves the processing and analysis of LiDAR data to reveal hidden or obscured archaeological features. By using advanced software tools, archaeologists can filter out vegetation and other surface elements from the point cloud data, exposing the underlying topography and any potential structures. This process allows researchers to identify, map, and study ancient structures with a level of detail and accuracy that was previously unattainable through traditional survey methods.
Advantages of Using LiDAR in Archaeology
Speed and Efficiency
One of the most significant benefits of using LiDAR in archaeology is its ability to cover large areas quickly and efficiently. Traditional survey methods, such as ground-penetrating radar or manual excavation, can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. In contrast, LiDAR-equipped drones can survey extensive sites in a matter of hours, significantly reducing the time and resources required to gather valuable data.
Non-Invasive Method
LiDAR is a non-invasive, non-destructive method of gathering information about archaeological sites. This feature makes it an ideal tool for surveying sensitive areas where excavation or other intrusive techniques could potentially damage valuable artifacts or disturb the landscape. By capturing detailed data from above, LiDAR allows archaeologists to study and preserve the site without causing any harm.
High-Resolution Data
LiDAR technology generates high-resolution, accurate data that can reveal subtle features of the landscape and archaeological structures. By collecting millions of data points, LiDAR can create detailed 3D models of the terrain and uncover hidden features that may not be visible through traditional survey methods. This high-resolution data allows archaeologists to study and analyze sites with greater precision and depth.
Revealing Hidden Features
One of the most notable advantages of LiDAR in archaeology is its ability to penetrate vegetation and other surface elements, revealing hidden structures and features beneath. Dense forests, undergrowth, and soil layers can obscure archaeological sites, making them difficult or impossible to detect using conventional methods. LiDAR technology can effectively “see through” these obstacles, exposing the underlying landscape and enabling researchers to discover previously unknown sites.
LiDAR for Archaeological Research
LiDAR has proven to be a valuable tool for archaeological research, enabling scholars to gain new insights into ancient civilizations and their environments. By providing accurate, high-resolution data, LiDAR technology has revolutionized the study of past cultures, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and a deeper understanding of human history.
Limitations of LiDAR in Archaeology
Technical Limitations
Despite its many advantages, LiDAR technology does have some limitations in the field of archaeology. For example, LiDAR may not be as effective in detecting features beneath dense tree canopies or in areas with thick undergrowth. Additionally, while LiDAR can penetrate vegetation to some extent, it cannot penetrate solid surfaces like soil or rock, which can limit its effectiveness in certain contexts.
Ethical Considerations
The use of LiDAR in archaeology also raises ethical concerns, particularly regarding the potential for the technology to reveal sensitive or culturally significant sites. The widespread availability of LiDAR data can lead to unauthorized excavations, looting, or damage to archaeological sites. As a result, researchers must carefully consider the ethical implications of their work and collaborate with local communities to ensure the responsible use of LiDAR data.
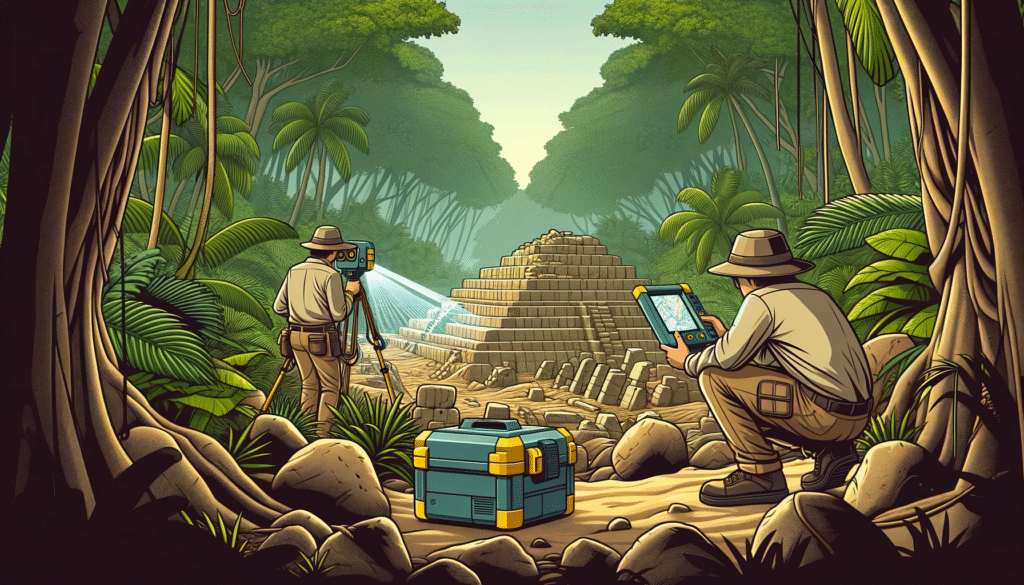

How has LiDAR Changed the Way We Study Archaeological Sites?
Case Studies: Successful Applications of LiDAR in Archaeology
Angkor Wat, Cambodia
LiDAR technology has played a crucial role in uncovering the hidden urban landscape surrounding the famous Angkor Wat temple complex in Cambodia. In 2012, an extensive LiDAR survey revealed a vast, interconnected network of roads, canals, and previously unknown temples hidden beneath the dense jungle. These findings have transformed our understanding of the ancient Khmer civilization and its urban planning, leading to new insights into the culture’s decline and ultimate collapse.
Mayan Ruins, Central America
In Central America, LiDAR technology has been instrumental in revealing the true extent of the ancient Maya civilization. A 2018 LiDAR survey conducted in Guatemala uncovered over 60,000 previously unknown structures, including houses, fortifications, and agricultural terraces. These discoveries have significantly changed our understanding of the scale and complexity of Maya cities, suggesting that their populations were much larger and more interconnected than previously believed.
Stonehenge, England
LiDAR has also been employed to study the iconic Stonehenge monument in England. By mapping the surrounding landscape in high resolution, researchers have identified previously unknown features, such as hidden pits and burial mounds. This data has provided valuable insights into the monument’s construction, purpose, and the ancient society that built it.
LiDAR Technology in the Archaeology Industry
Future Advancements and Prospects
As LiDAR technology continues to evolve, its applications in archaeology are expected to expand even further. Improvements in sensor technology, data processing, and drone capabilities will enable researchers to capture even more detailed and accurate data, leading to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of our shared past.
One promising development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms with LiDAR data processing. These advanced techniques can help automate the identification and mapping of archaeological features, allowing researchers to analyze vast amounts of data more efficiently and accurately.
Furthermore, advances in visualization technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR), offer exciting possibilities for bringing LiDAR-generated 3D models to life. These immersive tools can provide new ways for researchers, students, and the public to explore and experience archaeological sites, fostering a deeper appreciation and understanding of our cultural heritage.
As the adoption of LiDAR technology in archaeology continues to grow, it is crucial for researchers, governments, and industry professionals to work together to address the ethical considerations and ensure that this powerful tool is used responsibly and to its full potential. By embracing the possibilities offered by LiDAR and other emerging technologies, the archaeology industry can continue to advance our knowledge of human history and enrich our connection to the past.
In summary, LiDAR drone scanning has transformed the field of archaeology, offering a powerful and non-invasive method to uncover hidden treasures and reveal the secrets of the past. Its numerous applications and benefits make it an invaluable tool for archaeologists worldwide. To learn more about LiDAR technology and its wide-ranging applications, don’t miss our comprehensive guide on Aerial LiDAR 101: An Introduction to Its Applications and Benefits.
If you’re in need of professional drone services for your archaeological project or any other purpose, Blue Falcon Aerial is here to help. Our team of experts is ready to assist you with cutting-edge technology and unparalleled expertise. Contact us today to discuss your needs and discover how we can bring your vision to life.




